Node Js Aws Lambda Read Environment Variables
AWS Lambda is a service that confuses many people. For that reason, you may be wondering but how it works, and how you lot'd use it to build a highly scalable event-driven application. Every bit someone who'south presumably no stranger to the internet, you must have seen the terms serverless, function-as-a-service, or AWS Lambda thrown across your screen a few times. Perhaps you lot're looking to acquire more than.
If so, you lot're in luck. In this postal service, y'all'll learn virtually AWS Lambda, serverless, and how to build a scalable paradigm processing app using AWS Lambda and Node.js.
What is serverless?
First, let me have y'all back to the time when applications were hosted on physical machines in server rooms. Back then, companies congenital their own data centers. The procedure was tedious, hard, and very demanding.
Recently, a new era paved the way for running an awarding in the cloud. You no longer needed to entertain the idea of building your own information centers anymore.
Later on all, why would yous?
In just minutes, you could spin up servers in multiple regions and deploy applications in seconds. However, server provisioning, scaling, and monitoring was still a hard chore.
At present, a shift in cloud computing known as serverless, or function-as-a service, has emerged in parallel. There is no need for server provisioning, monitoring, logging, or managing the underlying infrastructure. Instead, the focus is on your business organization logic, broken downwardly into smaller, single-purpose functions like then:
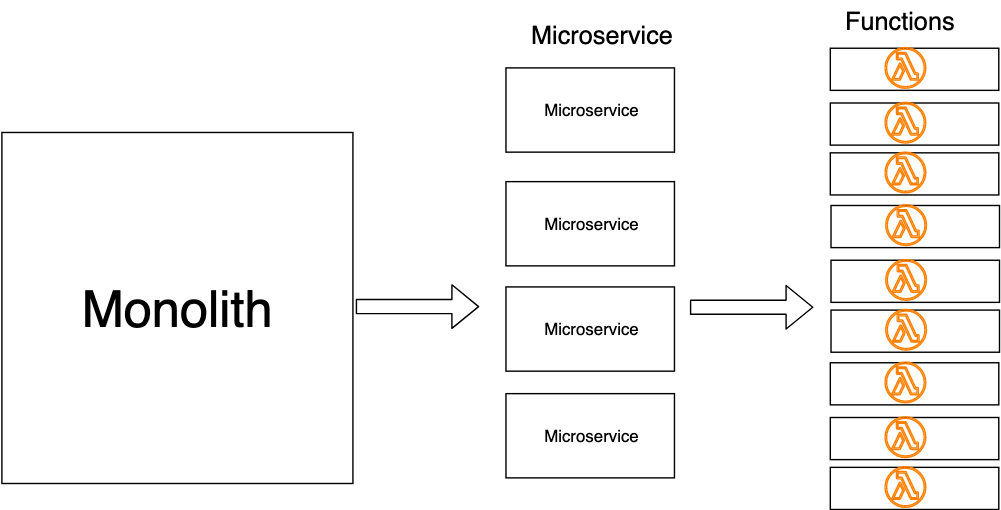
Serverless doesn't mean an absence of servers, because there actuallyare servers. It only means the burden of managing these servers is taken abroad from you.
I of the entities responsible for taking intendance of these servers is Amazon Web Services.
What's Amazon Web Services?
Amazon Web Service, or AWS, is a leader in cloud computing platforms.
According to their website, AWS provides a "highly reliable, scalable, low-cost infrastructure platform and powers hundreds of thousands of businesses in 190 countries around the world." According to Canalys' 2018 report, AWS holds 32.6% of the marketplace share. That'south more than what's held by whatsoever other provider.
With that established, now's the time to agree onto your lid. That's because you're going to learn something cool—no, somethingmind-blowing.
AWS Lambda functions
As I said in the commencement, Lambda is a calculating service offered by AWS. It allows you to run code without having to deal with servers in the cloud. An event triggers a Lambda function and dies after execution.
The Lambda function just does one thing. Information technology could be something as simple as retrieving a blog postal service, creating a blog postal service, or even sending an email.
There are three ways you could create a Lambda function on AWS:
- You lot could use the AWS panel. This is a web interface provided past AWS for managing and accessing their services. Withal, I don't typically recommend this method because it's very hard to write a total-fledged application from the console.
- You could use the deject-based IDE AWS provides. This lets you write, run, and debug your code from your browser.
- You could use your local development surround with your editor of option and, of course, deploy to live with ane command. Uncomplicated!We'll be exploring the third option in this post.
Endeavor Stackify's gratuitous lawmaking profiler, Prefix, to write better code on your workstation. Prefix works with .Internet, Java, PHP, Node.js, Ruby, and Python.
How to create an AWS account
Every Lambda function is preceded by an AWS account, and then you lot'll need to have one. The requirements for an account are simple.
- Valid e-mail address
- Phone number
- Valid credit card
Don't worry; you don't need to pay annihilation. AWS offers a free tier account. With this programme, y'all tin use almost all of AWS's services without paying a dime for one year.
To set upwardly your free business relationship,
- Go to the AWS console.
- Click onCreate a Costless Business relationship.
- Fill in your electronic mail address and, of course, a strong password.
- Fill in your contact details.
- Enter your payment information using a valid credit carte du jour.
- Complete the identity verification process by answering Amazon'southward telephone call.
- You'll see a 4-digit number on your browser screen. Enter it on your telephone keypad.
- Select the complimentary support program.
- Congratulations! You can at present sign in to your brand new AWS account.
Setting up your local development environment
We're going to use the Serverless framework, a CLI tool written in Node.js that lets you write and deploy Lambda functions. It supports many providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, IBM OpenWhisk, Google Cloud Platform, Kubeless, Spotinst, and more.
The Serverless framework is easy to install. Showtime, you lot demand a Node.js runtime. Now, I must remind you to install a version of Node.js supported by AWS Lambda. I'll stick to Node.js 8.10 runtime in this post.
Yous'll also desire to ensure your local environs is every bit close to the production environment as possible. This includes the runtime.
If yous take other versions installed already, you lot can utilize NVM to install Node.js 8.10 runtime or switch betwixt versions of Node.js.
$ nvm install v8.x
If you want to switch between versions of Node.js, you lot'd do this:
$ nvm use viii.x
Now that yous take Node.js runtime, proceed to install the Serverless framework:
$ npm install -g serverless
Check that the Serverless framework was installed.
$ serverless --version 1.xl.0
How to create a programmatic user on AWS
Your Lambda function won't live on your local surround forever. It needs to get into an AWS environment before the magic can happen. I refer to this process as deployment. The Serverless framework needs a mode to access AWS resources and deploy your functions on your behalf.
For this purpose, you'll need a programmatic user account. This account won't be able to log in to AWS console. Rather, it'll access AWS resources through API calls using access keys we'll create soon.
I've provided easy steps to create a programmatic user below.
1. Login to AWS console and go toIAM user:
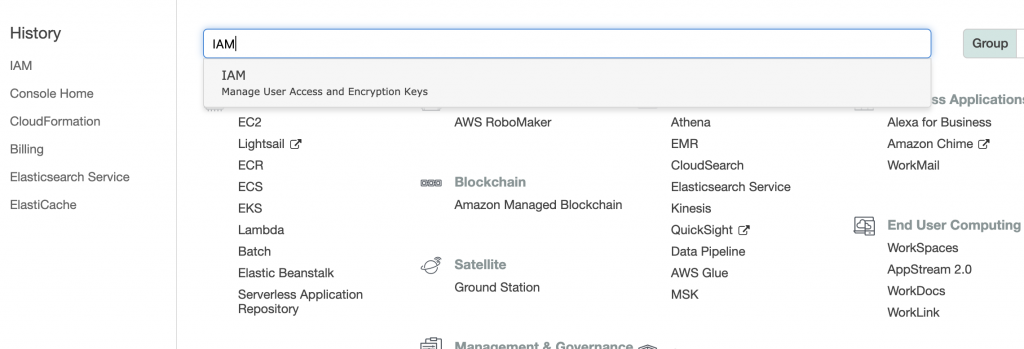
2. Click onAdd together user to begin the user creation process:
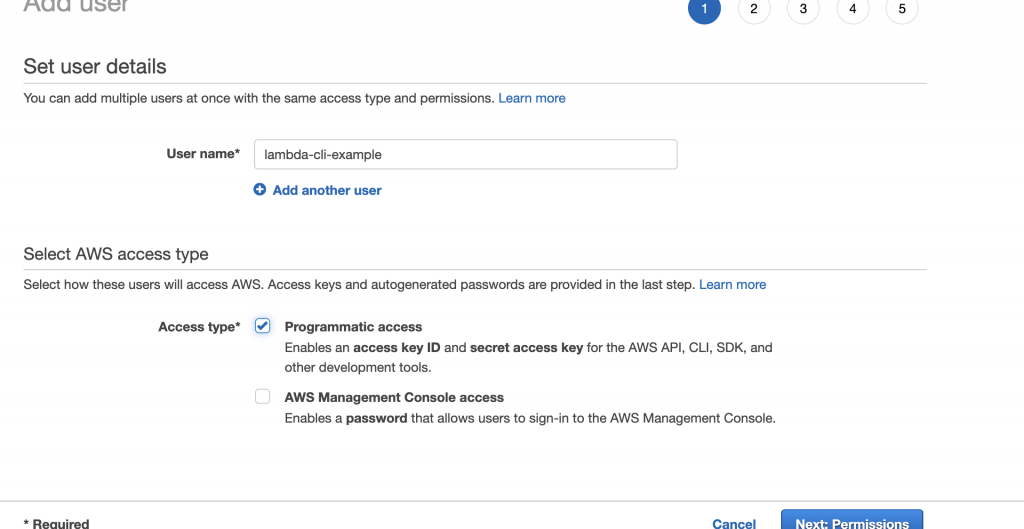
3. Type inlambda-example-cli equally the user name, enable programmatic access by checking the checkbox, and click onSide by side: permissionsto proceed.
4. Click onAdhere existing policy direct and search forAmbassador admission. SelectAdministratorAccess by checking the box. A policy is an object in AWS that defines the permissions of a user, part, or group.
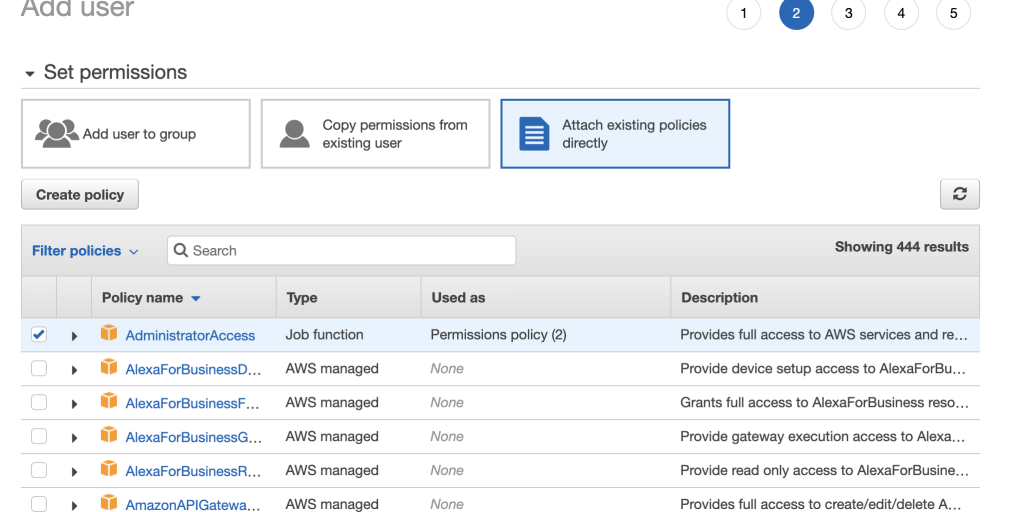
v. Review your choices and and so click on theCreate user button. Yous should see this screen.
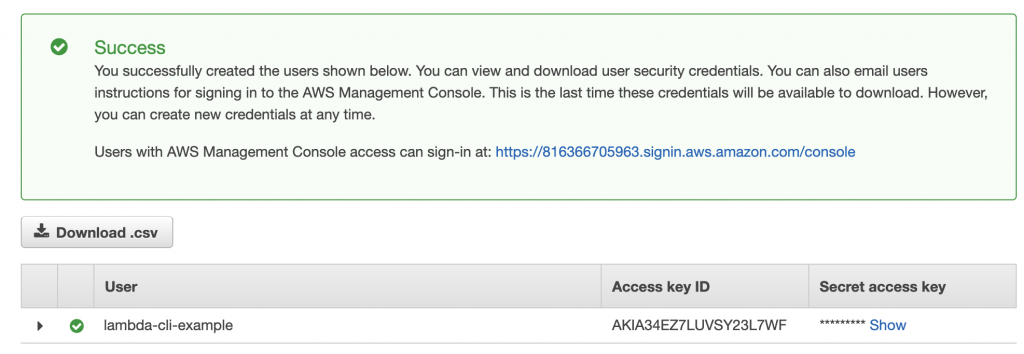
seven. Copy or download a CSV file containing your access key ID and access fundamental secret. Yous need to keep this secure.
I echo, keep it safe.
Anyone with admission to these keys tin make API calls like yous would. They can control and use your AWS account.
8. Configure serverless CLI with your AWS credentials. This is necessary for deployment.
serverless config credentials --provider aws --key <your_access_key_id> --secret <your_access_key_secret>
Your kickoff Lambda app with Node.js
Now, we'll create a unproblematic howdy world app. Then, we'll create a more avant-garde app that downloads an image from a URL, resizes it, and then uploads it to AWS S3, which is a highly scalable object storage service.
First, nosotros'll offset by using the Serverless CLI tool to bootstrap our project:
$ serverless create --template hullo-earth
If you ran the control in a higher place successfully, y'all should already have ii files created for you.
. ├── handler.js └── serverless.yml
We supplied the–template argument to let Serverless CLI know our choice of templates. There are dozens of templates the Serverless CLI tool supports. You tin can find them in this repository.
Handler.js
Now,handler.js is the Lambda function. This is where your logic stays.
'use strict'; module.exports.helloWorld = (event, context, callback) => { ... This role accepts three arguments: result, context, and a callback.
Consequence
The event argument contains consequence data. In that location are dissimilar event types, and each often contains different attributes. Agreement how Lambda functions work can be a bit hard to grasp at first.
The first matter to notation is that a Lambda function has to be triggered by a service and cannot run on its own. You'll detect a list of services that are capable of invoking Lambda functions here.
Context
Employ the context argument to pass the runtime parameter to the Lambda office.
Callback
Use the callback statement to return responses to the caller.
Serverless.yml
The fileserverless.yml contains your API definition and other resources. These are the services your application depends on to work equally expected. Later in this post, nosotros'll need an S3 bucket to shop images.
Let's make some modifications toserverless.yml. Nosotros'll change the runtime property tonodejs8.10. Then, nosotros'll add together a new property,region, to the provider object which will deploy the app to the region we specify. This is completely optional, and AWS will default tous-due east-1 if not specified. It's important to choose regions shut to your users in product considering of latency.
service: serverless-hello-earth # The `provider` cake defines where your service volition be deployed provider: name: aws runtime: nodejs8.10 region: eu-west-ane ....
How to deploy the app
We deploy the app with adeploy argument. From the console, execute the control below:
$ serverless deploy
On completion, you'll see the output in your console. The of import thing to note hither is the endpoint.
... api keys: None endpoints: Become - https://ss7n639ye3.execute-api.european union-west-1.amazonaws.com/dev/hullo-world functions: helloWorld: serverless-hello-world-dev-helloWorld ...
If you access the endpoint from your browser, you should meet your request printed back to y'all. Congratulations! You lot just built your first Lambda app.
Going further
The famous hello globe app we built in a previous section was pretty simple. Now, it's time to go a piffling further by building something more advanced.
Nosotros'll build a Lambda app that gets images from a URL, resizes them on the fly, and uploads them to an S3 saucepan, every bit I said earlier. You can modify the previous hello earth app or start a new project from scratch.
We'll brand changes toserverless.yml as follows:
# filename: serverless.yml service: ImageUploaderService # The `provider` block defines where your service will be deployed custom: bucket: getting-started-lambda-example provider: proper noun: aws runtime: nodejs8.10 region: eu-west-1 stackName: imageUploader iamRoleStatements: - Event: "Allow" Action: - "s3:PutObject" Resources: - "arn:aws:s3:::${cocky:custom.bucket}/*" # The `functions` block defines what lawmaking to deploy functions: UploadImage: handler: uploadImage.handler # The `events` block defines how to trigger the uploadImage.handler code events: - http: path: upload method: mail cors: true environment: Bucket: ${self:custom.bucket} resources: Resource: StorageBucket: Type: "AWS::S3::Bucket" Properties: BucketName: ${self:custom.bucket} What we accept here is a custom object in the YAML file where we define the saucepan's name of the bucket. You should cull a different saucepan name; you won't be able to employ the bucket name I used in this example unless I delete it. The AWS documentation says, "an Amazon S3 bucket name is globally unique, and the namespace is shared past all AWS accounts. This means that after a saucepan is created, the name of that bucket cannot be used by another AWS account in any AWS Region until the bucket is deleted."
If you expect further, you'll see that nosotros defined thestackName equallyImageUploader. A stack is a collection of AWS resources that ane tin can manage as a single unit. We likewise specified a globalIamRoleStatement. A Lambda function needs permissions to admission other AWS resource. In our example, we need permission to write to an S3 bucket. This permission is provided in the IAM office statements.
Below the Lambda functionUploadImage, we added a new object chosensurroundings. With this, we can set environment variables that we tin can get via theprocess.env object during execution. Delight take note of the handler's name.
Finally, we wrapped it up by defining an S3 bucket resources where the images volition exist stored.
Adding npm packages
You don't have to reinvent the wheel. Y'all can use your favorite npm packages in Lambda apps. They'll be packaged along with your functions on deployment.
We'll apply an npm package calleduuid to generate unique names for images, and we'll usejimp for manipulating uploaded images.
First, we need abundle.json file.
npm init
Y'all'll be asked some questions. Simply go alee and respond them.
npm install jimp uuid
Now, let's update the handler function. Don't forget to rename the role touploadImage.js. It's a good idea to name your office later on what information technology does.
// filename: uploadImage.js "employ strict"; const AWS = require("aws-sdk"); const uuid = crave("uuid/v4"); const Jimp = require("jimp"); const s3 = new AWS.S3(); const width = 200; const meridian = 200; const imageType = "epitome/png"; const bucket = process.env.Bucket; module.exports.handler = (effect, context, callback) => { let requestBody = JSON.parse(event.body); let photoUrl = requestBody.photoUrl; let objectId = uuid(); let objectKey = `resize-${width}ten${height}-${objectId}.png`; fetchImage(photoUrl) .and then(epitome => image.resize(width, elevation) .getBufferAsync(imageType)) .and so(resizedBuffer => uploadToS3(resizedBuffer, objectKey)) .then(function(response) { console.log(`Epitome ${objectKey} was uploaed and resized`); callback(null, { statusCode: 200, body: JSON.stringify(response) }); }) .catch(error => console.log(error)); }; /** * @param {*} data * @param {string} key */ function uploadToS3(information, key) { render s3 .putObject({ Bucket: saucepan, Key: key, Body: data, ContentType: imageType }) .promise(); } /** * @param {url} * @returns {Promise} */ function fetchImage(url) { return Jimp.read(url); ) If you look atuploadImage.js, you tin can encounter we take methodfetchImage responsible for getting the image from a URL.
You can read more about jimp packet's inner workings in their readme file.
After a resize, nosotros upload to our S3 bucket using theputObject method in the AWS SDK.
How to log in AWS Lambda functions
Logging gives visibility into how applications run in product. It can relieve you a lot of time when troubleshooting a problem.
While there are many log aggregating services, similar Retrace, AWS Cloudwatch and Lambda functions work well together.
Out of the box, AWS Lambda monitors functions on your behalf and reports metrics through Amazon CloudWatch. These metrics include full requests, duration, and error rates. Aside from the monitoring and logging provided, you can also log an event from your lawmaking withconsole.log:
panel.log('An error occurred') In our handler function (that is,uploadImage.js), we log to AWS CloudWatch when an image is processed successfully and when an error occurs.
Deploying and testing
Whether you're updating an existing awarding or deploying a new application, you deploy with theserverless deploycontrol:
serverless deploy
Your output volition be similar to the i shown below (and please do take note of the endpoint):
..... None endpoints: Mail - https://0sdampzeaj.execute-api.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/dev/upload functions: UploadImage: ImageUploaderService-dev-UploadImage layers:
If yous make a gyre request to this endpoint with the correct request trunk, the prototype is downloaded from the URL, resized, and uploaded to S3 bucket. Remember to change the post endpoint to the one in your console.
gyre -H "Content-type: awarding/json" -d '{"photoUrl":"https://www.petmd.com/sites/default/files/what-does-it-mean-when-cat-wags-tail.jpg"}' 'https://0sdampzeaj.execute-api.eu-westward-1.amazonaws.com/dev/upload' You can now see the logs in CloudWatch and your images in the S3 bucket.
Summary
Today, you learned about AWS and how to create an AWS account with access keys. You as well built your first hello world app running in the cloud, and you learned so much about the Serverless framework! Yous even proceeded to create a photo processing app.
That's a lot of basis to cover for a beginner.
To build on this noesis, consider learning more about Serverless framework and how to examination for Lambda functions. Yous should have a look at a post called "Serverless Local Development" by Gareth McCumskey, a spider web and Serverless developer. And if you desire to take a await at the lawmaking, yous tin find it on the Git repository.
From there, yous should exist well on your way to a consummate agreement of AWS Lambda with Node.js!
- Most the Author
- Latest Posts
hoseytheitheave1946.blogspot.com
Source: https://stackify.com/aws-lambda-with-node-js-a-complete-getting-started-guide/
0 Response to "Node Js Aws Lambda Read Environment Variables"
Publicar un comentario